MongoDB Getting Started
what is MongoDB
MongoDB is a document database. It stores data in a type of JSON format called BSON. A record in MongoDB is a document, which is a data structure composed of key value pairs similar to the structure of JSON objects.
A MongoDB Document
Records in a MongoDB database are called documents, and the field values may include numbers, strings, booleans, arrays, or even nested documents.
Example of MongoDB Document
{
title: "Post Title 1",
body: "Body of post.",
category: "News",
likes: 1,
tags: ["news", "events"],
date: Date()
}Getting Started
MongoDB is a document database and can be installed locally or hosted in the cloud.
SQL vs MongoDB
SQL databases are considered relational databases. They store related data in separate tables. When data is needed, it is queried from multiple tables to join the data back together.
MongoDB is a document database which is often referred to as a non-relational database. This does not mean that relational data cannot be stored in document databases. It means that relational data is stored differently. A better way to refer to it is as a non-tabular database. MongoDB stores data in flexible documents. Instead of having multiple tables you can simply keep all of your related data together. This makes reading your data very fast. You can still have multiple groups of data too. In MongoDB, instead of tables these are called collections.
Local vs Cloud Database
MongoDB can be installed locally, which will allow you to host your own MongoDB server on your hardware. This requires you to manage your server, upgrades, and any other maintenance.
You can download and use the MongoDB open source Community Server on your hardware for free.
For this post we are going to use MongoDB Atlas, a cloud database platform. This is much easier than hosting your own local database.
To be able to experiment with the code examples, you will need access to a MongoDB database.
Sign up for a free MongoDB Atlas account to get started.
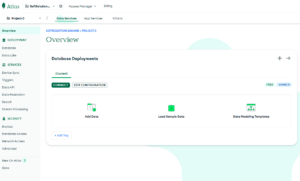
sign in and flow the instructions and when you have filled in your userId and Password, and chose a free Mongodb then you see the following:
Creating a Cluster
After you have created your account, set up a free “Shared Cluster” then choose your preferred cloud provider and region.
By default, MongoDB Atlas is completely locked down and has no external access.
You will need to set up a user and add your IP address to the list of allowed IP addresses.
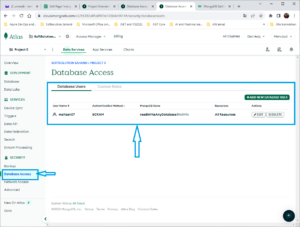
Under “Database Access”, create a new user and keep track of the username and password.
Next, under “Network Access”, add your current IP address to allow access from your computer.
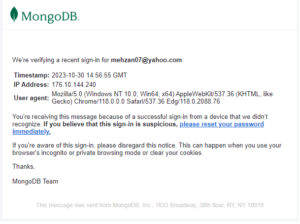
After creating account/login or reseting password you can get an email with following information:
MongoDB Clusters
What are clusters in MongoDB?
In the context of MongoDB, “cluster” is the word usually used for either a replica set or a sharded cluster. A replica set is the replication of a group of MongoDB servers that hold copies of the same data; this is a fundamental property for production deployments as it ensures high availability and redundancy, which are crucial features to have in place in case of failovers and planned maintenance periods.
A sharded cluster is also commonly known as horizontal scaling, where data is distributed across many servers.
The main purpose of sharded MongoDB is to scale reads and writes along multiple shards.
What is MongoDB Atlas Cluster?
MongoDB Atlas Cluster is a NoSQL Database-as-a-Service offering in the public cloud (available in Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, Amazon Web Services). This is a managed MongoDB service, and with just a few clicks, you can set up a working MongoDB cluster, accessible from your favorite web browser.
You don’t need to install any software on your workstation as you can connect to MongoDB directly from the web user interface as well as inspect, query, and visualize data.
Alternatively, if you prefer working with the command line, you can connect using the mongo shell. To do this, you’ll need to configure the firewall from the web portal to accept your IP. From the homepage, navigate to Security and then Network Access. Finally, click on “Add IP Address” and add your IP:
What is MongoDB replication
In simple terms, MongoDB replication is the process of creating a copy of the same data set in more than one MongoDB server. This can be achieved by using a Replica Set. A replica set is a group of MongoDB instances that maintain the same data set and pertain to any mongod process
Install MongoDB Shell (mongosh)
There are many ways to connect to your MongoDB database.
We will start by using the MongoDB Shell, mongosh.
Use the official instructions to install mongosh on your operating system, flow instructions step by step.
To verify that it has been installed properly, open your terminal and type:
mongosh --version
C:\Users\default1>mongosh --version 1.10.6
You should see that the latest version is installed.
Connect to the database
Go to the https://cloud.mongodb.com/ and then sign in with your userId and password then you shall have the following:
To connect to your database, you will need your database specific connection string.
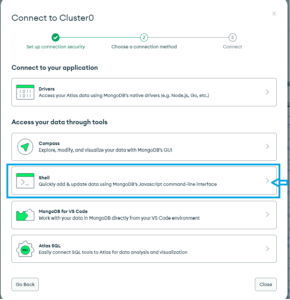
In the MongoDB Atlas dashboard, under “Databases”, click the “Connect” button for your Cluster.
Next, choose “Connect with the MongoDB Shell” as shown in the bellow:
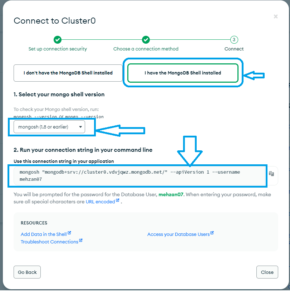
Then select My MongoDB Shall installed, and under dropdown of “Select your mongo shell version” and then copy the connection string under “2. Run your connection string in your command line” which is shown in the following figure:
Copy your connection string:
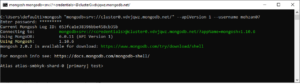
mongosh "mongodb+srv://cluster0.vdvjqwz.mongodb.net/" --apiVersion 1 --username mehzan07
Run this in Command line:
Now you are in the:
Atlas atlas-smbkyk-shard-0 [primary] test>
And you will receive email as follow:
In your Atlas Dashboard press to the Database Access then show you user information as the following:
From the Dashboard you can select any menu in the left side and use it.
Conclusion
In this post i have described about MongoDB, MongoDB Atlas, Creating Cluster, how to install MongoDB shell (Mongosh), how to login in and connect to Database
In my next post I am going to describe MongoDB Query API to interact with Database
This post is part of MongoDB-Step by step.